java中文件拷貝流的介紹
最近項(xiàng)目里有個需求需要實(shí)現(xiàn)文件拷貝,在java中文件拷貝流的讀寫,很容易就想到IO中的InputStream和OutputStream之類的,但是上網(wǎng)查了一下文件拷貝也是有很多種方法的,除了IO,還有NIO、Apache提供的工具類、JDK自帶的文件拷貝方法
創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)公司專注為客戶提供全方位的互聯(lián)網(wǎng)綜合服務(wù),包含不限于網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)制作、網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)、大東網(wǎng)絡(luò)推廣、小程序制作、大東網(wǎng)絡(luò)營銷、大東企業(yè)策劃、大東品牌公關(guān)、搜索引擎seo、人物專訪、企業(yè)宣傳片、企業(yè)代運(yùn)營等,從售前售中售后,我們都將竭誠為您服務(wù),您的肯定,是我們最大的嘉獎;創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)公司為所有大學(xué)生創(chuàng)業(yè)者提供大東建站搭建服務(wù),24小時服務(wù)熱線:18982081108,官方網(wǎng)址:m.2m8n56k.cn
IO拷貝
public class IOFileCopy {
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
public static void copyFile(String source, String target) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try(InputStream in = new FileInputStream(new File(source));
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File(target))) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
int len;
while ((len = in.read(buffer)) > 0) {
out.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println(String.format("IO file copy cost %d msc", System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
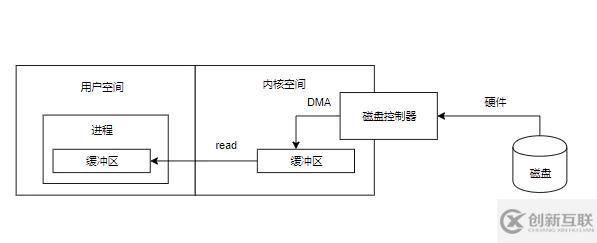
}傳統(tǒng)IO中文件讀取過程可以分為以下幾步:
內(nèi)核從磁盤讀取數(shù)據(jù)到緩沖區(qū),這個過程由磁盤操作器通過DMA操作將數(shù)據(jù)從磁盤讀取到內(nèi)核緩沖區(qū),該過程不依賴CPU
用戶進(jìn)程在將數(shù)據(jù)從內(nèi)核緩沖區(qū)拷貝到用戶空間緩沖區(qū)
- 用戶進(jìn)程從用戶空間緩沖區(qū)讀取數(shù)據(jù)
NIO拷貝
NIO進(jìn)行文件拷貝有兩種實(shí)現(xiàn)方式,一是通過管道,而是通過文件內(nèi)存內(nèi)存映射
public class NIOFileCopy {
public static void copyFile(String source, String target) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try(FileChannel input = new FileInputStream(new File(source)).getChannel();
FileChannel output = new FileOutputStream(new File(target)).getChannel()) {
output.transferFrom(input, 0, input.size());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(String.format("NIO file copy cost %d msc", System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}文件內(nèi)存映射:
把內(nèi)核空間地址與用戶空間的虛擬地址映射到同一個物理地址,DMA 硬件可以填充對內(nèi)核與用戶空間進(jìn)程同時可見的緩沖區(qū)了。用戶進(jìn)程直接從內(nèi)存中讀取文件內(nèi)容,應(yīng)用只需要和內(nèi)存打交道,不需要進(jìn)行緩沖區(qū)來回拷貝,大大提高了IO拷貝的效率。加載內(nèi)存映射文件所使用的內(nèi)存在Java堆區(qū)之外
public class NIOFileCopy2 {
public static void copyFile(String source, String target) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File(source));
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(target))) {
FileChannel sourceChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel targetChannel = fos.getChannel();
MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = sourceChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, sourceChannel.size());
targetChannel.write(mappedByteBuffer);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(String.format("NIO memory reflect file copy cost %d msc", System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
File targetFile = new File(target);
targetFile.delete();
}
}NIO內(nèi)存映射文件拷貝可以分為以下幾步
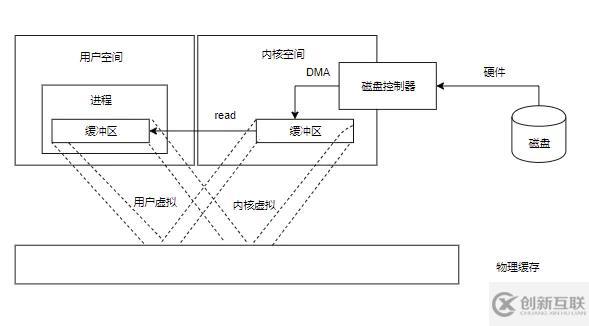
NIO的內(nèi)存映射實(shí)際上就是少了一次從內(nèi)核空間拷貝到用戶空間的過程,將對用戶緩沖區(qū)的讀改為從內(nèi)存讀取
Files#copyFile方法
public class FilesCopy {
public static void copyFile(String source, String target) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
File sourceFile = new File(source);
File targetFile = new File(target);
Files.copy(sourceFile.toPath(), targetFile.toPath());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(String.format("FileCopy file copy cost %d msc", System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}FileUtils#copyFile方法
使用FileUtils之前需先引入依賴
依賴
<dependency> <groupId>commons-io</groupId> <artifactId>commons-io</artifactId> <version>2.4</version> </dependency>FileUtils#copyFile封裝類:FileUtilsCopy.java
public class FileUtilsCopy { public static void copyFile(String source, String target) { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { FileUtils.copyFile(new File(source), new File(target)); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(String.format("FileUtils file copy cost %d msc", System.currentTimeMillis() - start)); } }
性能比較
既然有這么多種實(shí)現(xiàn)方法,肯定要從中選擇性能最佳的
測試環(huán)境:
- windows 10
- CPU 6核
- JDK1.8
測試代碼:PerformTest.java
public class PerformTest {
private static final String source1 = "input/test1.txt";
private static final String source2 = "input/test2.txt";
private static final String source3 = "input/test3.txt";
private static final String source4 = "input/test4.txt";
private static final String target1 = "output/test1.txt";
private static final String target2 = "output/test2.txt";
private static final String target3 = "output/test3.txt";
private static final String target4 = "output/test4.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) {
IOFileCopy.copyFile(source1, target1);
NIOFileCopy.copyFile(source2, target2);
FilesCopy.copyFile(source3, target3);
FileUtilsCopy.copyFile(source4, target4);
}
}總共執(zhí)行了五次,讀寫的文件大小分別為9KB、23KB、239KB、1.77MB、12.7MB
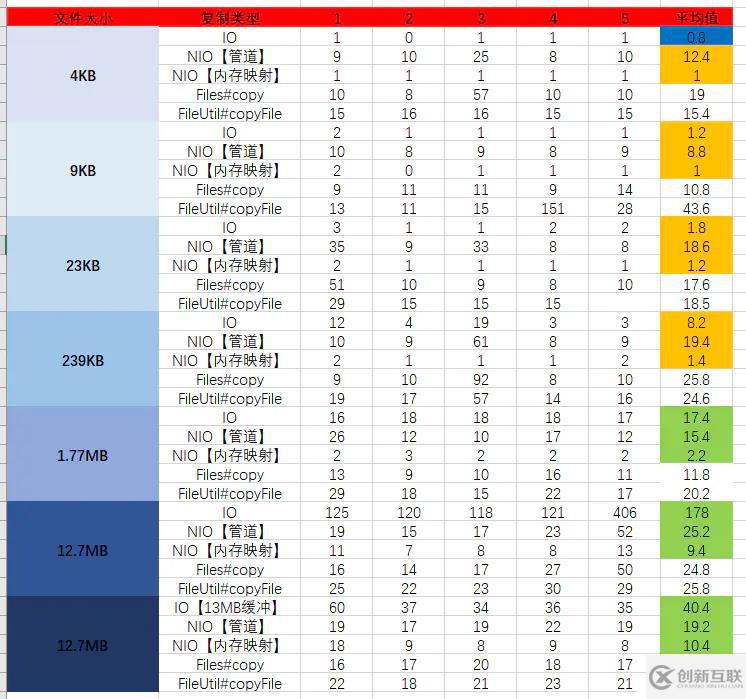
注意:單位均為毫秒
從執(zhí)行結(jié)果來看:
文件很小時 => IO > NIO【內(nèi)存映射】> NIO【管道】 > Files#copy > FileUtils#copyFile
在文件較小時 => NIO【內(nèi)存映射】> IO > NIO【管道】 > Files#copy > FileUtils#copyFile
在文件較大時 => NIO【內(nèi)存映射】> > NIO【管道】> IO > Files#copy > FileUtils#copyFile
- 修改IO緩沖區(qū)大小對拷貝效率有影響,但是并不是越大性能越好,稍大于拷貝文件大小即可
文件較小時,IO效率高于NIO,NIO底層實(shí)現(xiàn)較為復(fù)雜,NIO的優(yōu)勢不明顯。同時NIO內(nèi)存映射初始化耗時,所以在文件較小時和IO復(fù)制相比沒有優(yōu)勢
如果追求效率可以選擇NIO的內(nèi)存映射去實(shí)現(xiàn)文件拷貝,但是對于大文件使用內(nèi)存映射拷貝要格外關(guān)注系統(tǒng)內(nèi)存的使用率。推薦:大文件拷貝使用內(nèi)存映射,原文是這樣的:
For most operating systems, mapping a file into memory is more
expensive than reading or writing a few tens of kilobytes of data via
the usual {@link #read read} and {@link #write write} methods. From the
standpoint of performance it is generally only worth mapping relatively
large files into memory絕大多數(shù)操作系統(tǒng)的內(nèi)存映射開銷大于IO開銷
網(wǎng)站欄目:java中文件拷貝流的介紹
URL地址:http://m.2m8n56k.cn/article22/jdsccc.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站、電子商務(wù)、手機(jī)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)、靜態(tài)網(wǎng)站、搜索引擎優(yōu)化、網(wǎng)頁設(shè)計(jì)公司
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點(diǎn)不代表本網(wǎng)站立場,如需處理請聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時需注明來源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 企業(yè)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)基于用戶體驗(yàn)的網(wǎng)頁UI設(shè)計(jì) 2016-09-15
- 怎么才能做出一份優(yōu)秀的網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)方案 2021-03-20
- 企業(yè)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)選擇響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì) 2013-10-08
- 企業(yè)網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)主要原則 2022-07-26
- 網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)公司應(yīng)具備哪些特質(zhì)以及如何與客戶有效的溝通呢? 2022-05-11
- 成都網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)是做什么的?就業(yè)前景如何? 2022-06-06
- 電商網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)需要把控的問題 2022-10-23
- 什么是網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)?網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)和其他設(shè)計(jì)的區(qū)別與關(guān)聯(lián) 2022-05-13
- 影響網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)優(yōu)化的因素都有哪些? 2021-05-31
- 網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)需要注意哪些問題 2023-03-10
- 質(zhì)量超好的上海網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司、上海網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)公司網(wǎng)站建設(shè) 2020-11-07
- 安福手機(jī)網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)在制作時要做哪些工作 2020-12-14